39 zero coupon bonds risk
Zero Coupon Bonds - Taxation, Advantages & Disadvantages - Fisdom Trust factor of Issuer: Since zero-coupon bonds have lengthy maturity periods, it can be challenging for investors to continue their trust in the issuer till the maturity date arrives. Interest Rate Risk: Zero-coupon bonds that are sold before maturity are subject to interest rates risk. This is because the value of these bonds is inversely proportional to interest rates. Zero-Coupon Bonds and Taxes - Investopedia The zero-coupon bond has no such cushion, faces higher risk, and makes more money if the issuer survives. Zero-Coupon Bonds and Taxes Zero-coupon bonds may also appeal to investors looking to pass...
calculator.me › savings › zero-coupon-bondsZero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to ... Economist Gary Shilling mentioned holders of 30-year zero-coupon bonds purchased in the early 1980s outperformed the SP 500 with dividends reinvested by 500% over the subsequent 30-years as interest rates fell from around 14.6% to around 3%. I started investing in 30 Year zero coupon treasuries. Now, zero coupon bonds don't pay any interest ...

Zero coupon bonds risk
› terms › zZero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia May 31, 2022 · Zero-Coupon Bond: A zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full ... › articles › investingAdvantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Unique Risks of Zero-Coupon U.S. Treasury Bonds Because of their sensitivity to interest rates, zero-coupon Treasury bonds have incredibly high interest rate risk. Treasury zeros fall significantly... Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to … Economist Gary Shilling mentioned holders of 30-year zero-coupon bonds purchased in the early 1980s outperformed the SP 500 with dividends reinvested by 500% over the subsequent 30-years as interest rates fell from around 14.6% to around 3%. I started investing in 30 Year zero coupon treasuries. Now, zero coupon bonds don't pay any interest ...
Zero coupon bonds risk. Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia May 31, 2022 · Zero-Coupon Bond: A zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full ... Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds. Understanding Zero-Coupon Bonds As a zero-coupon bond does not pay periodic coupons, the bond trades at a discount to its face value. › glossary › zero-coupon-bondZero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don't mature for ten, fifteen, or more years. Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. That definition assumes a positive time value of money. It does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par value. Examples of zero-coupon bonds include US Treasury bills, US savings bonds, long-term zero-coupon bonds, and any type of coupon bond that has been stripped of its coupons. Zero coupon
Understanding Bonds: The Types & Risks of Bond Investments Zero-coupon bonds and Treasury bills are exceptions: The interest income is deducted from their purchase price and the investor then receives the full face value of the bond at maturity. All bonds carry some degree of "credit risk," or the risk that the bond issuer may default on one or more payments before the bond reaches maturity. What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? - The Motley Fool With zero-coupon bonds, interest rate risk is at its highest since zeros display unusual sensitivity to changes in interest rates -- although the underlying inverse relationship to interest rates... What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks As a result, zero-coupon bond prices are more volatile — subject to greater swings when interest rates change. You have to pay taxes on income you don't get Even though you're not actually getting... Zero-Coupon Bonds: Pros and Cons - Management Study Guide This is the reason why zero-coupon bonds have a higher annualized yield as compared to other bonds. This works out to be beneficial for investors who do not have a need for receiving immediate payments. No Reinvestment Risk: Zero-coupon bonds do not have any reinvestment risk. This is because the bond does not pay interest periodically.
Zero-coupon bonds news and analysis articles - Risk.net Original research. The impact of compounding on bond pricing with alternative reference rates. This paper looks at the impact of compounding on zero-coupon bond prices by considering the short rate when it follows a Gaussian diffusion process or a stochastic volatility jump-diffusion process. 12 Oct 2021. › knowledge › zero-coupon-bondZero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Excel Calculator - Wall Street Prep Zero-coupon bonds are often perceived as long-term investments, although one of the most common examples is a “T-Bill,” a short-term investment. U.S. Treasury Bills (or T-Bills) are short-term zero-coupon bonds (< 1 year) issued by the U.S. government. Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula How Do Zero Coupon Bonds Work? - SmartAsset Even though you can earn more because you purchased the bond at a reduced rate, they do carry some risk. If interest rates rise, the value of zero coupon bonds can fall. If you sell before maturity, they are subjected to interest rate risk. Bottom Line. Zero coupon bonds, just like other bonds and securities, carry risk. › investing › corporate-bondsCorporate Bonds: An Introduction to Credit Risk - Investopedia Apr 29, 2021 · Corporate bonds offer a higher yield than some other fixed-income investments, but for a price in terms of added risk. Most corporate bonds are debentures, meaning they are not secured by ...
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don’t mature for ten ...
Managing Risk With Fixed Income: How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds Your principal is at risk the entire time. Buying individual bonds across the yield curve provides for a much more stable fixed income position. If rates go up and bond prices fall, you can simply hold your bonds until maturity, collecting coupons along the way and receive your principal back at the end.
Bonds Center - Bonds quotes, news, screeners and educational Bonds Center - Learn the basics of bond investing, get current quotes, news, commentary and more.
How to Calculate Yield to Maturity of a Zero-Coupon Bond Corporate zero-coupon bonds are usually riskier than similar coupon-paying bonds. If the issuer defaults on a zero-coupon bond, the investor has not even received coupon payments, so the potential...
The Allure Of Zero Coupon Municipal Bonds: A Low Risk Investment With ... 2) Zero coupon bonds do introduce more duration risk (i.e. they fall in value more as interest rates rise). If you feel that this is a threat, then zero coupon bonds are less attractive at the margin (because of the reinvestment ability that BK listed in straight (coupon-paying) bonds as interest rates rise - conversely, no reinvestment risk if yields fall.)
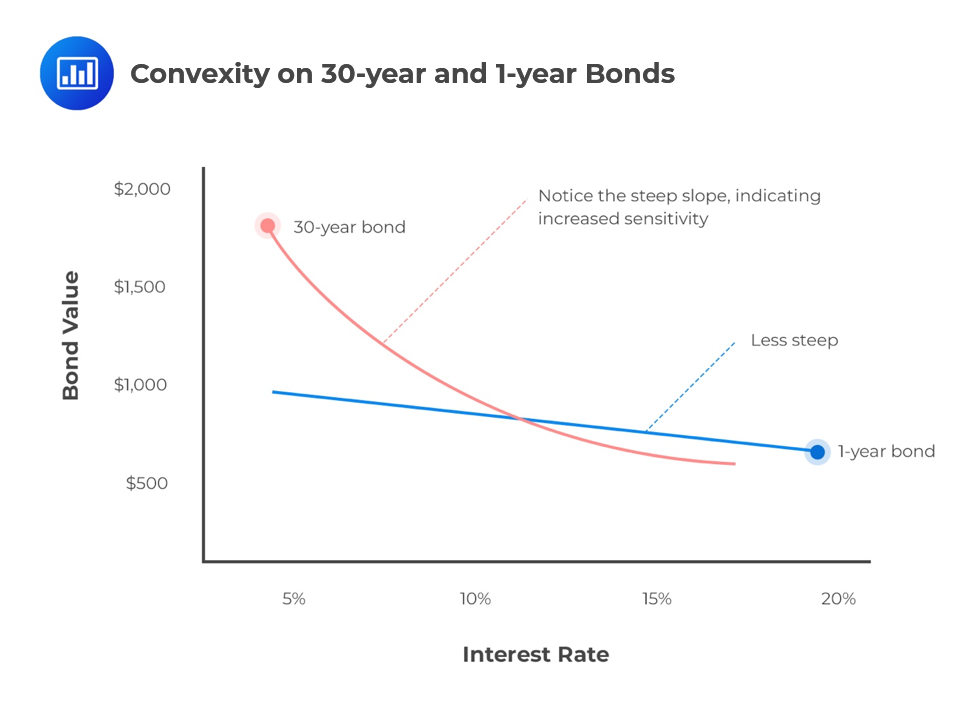
Zero-Coupon Bonds: Definition, Formula, Example ... - CFAJournal They are safe investment instruments, and have a lower element of risk involved. Long Dated zero coupon bonds are said to be the most responsive to interest rate fluctuations. Therefore, in case of longer time duration (a higher 'N'), it might prove to be profitable for the bond holder. Disadvantages of Zero-Coupon Bonds
What does it mean if a bond has a zero coupon rate? - Investopedia A zero coupon bond generally has a reduced market price relative to its par value because the purchaser must maintain ownership of the bond until maturity to turn a profit. A bond that sells for...



Post a Comment for "39 zero coupon bonds risk"