41 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
Advantages and Risks of Zero-Coupon US Treasury Bonds Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds are also known as Treasury zeros, and they often rise dramatically in price when stock prices fall. Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds can move up significantly when... What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond and a Treasury bill? T-bills are also called as zero coupon bond, which is issued at discount. T bills are short term instruments issued within one year. 91 days, 182 days, 364 days are the examples of maturity period. T-bills are issued by goverment of any country. One point to remember
What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond ... - Quora T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value ...

Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
Zero Coupon Bond Funds: What Are They? - The Balance A zero coupon bond is a bond that doesn't offer interest payments but sells at a discount—a price lower than its face value. 1 The bondholder doesn't get paid while they own the bond, but when the bond matures, they will be repaid the full face value. Zero coupon bond funds are funds that hold these types of bonds. Treasury Bills (T-Bills) - Meaning, Examples, Calculations Treasury bills are a type of zero-coupon security where the central government borrows funds from the individual for a period of 364 days or less. ... another route is through the issue of T-Bills and other bonds Bonds Bonds refer to the debt instruments issued by governments or corporations to acquire investors' funds for a certain period ... Can you lose money on Treasury notes? - Note Brokering Treasury bills are not like coupon bonds that pay interest in accruals. What are Treasury bills example? Treasury bills are zero-coupon securities and do not pay interest. They are issued at a discount and are redeemed at face value at maturity. For example, a 91-day treasury bill of Rs. 100 / - (nominal value) can be issued for example Rs. ...
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds. The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000. 14.3 Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Financial Accounting This zero-coupon bond was sold for $2,200 below face value to provide interest to the buyer. Payment will be made in two years. The straight-line method simply recognizes interest of $1,100 per year ($2,200/2 years). Figure 14.11 December 31, Years One and Two—Interest on Zero-Coupon Bond at 6 Percent Rate—Straight-Line Method Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula It is also called a pure discount bond or deep discount bond. U.S. Treasury bills are an example of a zero-coupon bond. Summary A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds. Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) Bonds are debt instruments also issued by the government or corporate for tenure equal to or more than 2 years period. T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value at the end of the tenure, which is the return on their investment.
What is the difference between a zero-coupon bond and a ... The difference between a regular bond and a zero-coupon bond is the payment of interest, otherwise known as coupons. A regular bond pays interest to ... why is treasury bill also called as zero coupon bonds - Brainly.in Treasury notes also referred to as Zero-Coupon Bonds. • They are available for a minimum of and in multiples of that amount. • A treasury bill is a short-term borrowing instrument used by the Indian government that has a maturity of less than a year. • Treasury bills, which are sold to banks and the general public, allow the government to ... Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1 Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: Issued at deep discount and redeemed at full face value Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Excel Calculator - Wall Street Prep U.S. Treasury Bills (or T-Bills) are short-term zero-coupon bonds (< 1 year) issued by the U.S. government. Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond - i.e. the present value (PV) - the first step is to find the bond's future value (FV), which is most often $1,000.
Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to Maturity ... Zero coupon bonds do not pay interest throughout their term. Instead interest is accrued throughout the bond's term & the bond is sold at a discount to par face value. ... Treasury bills, notes, bonds : 1 month Treasury bills: 2.17%: 2 month Treasury bills: 2.15%: 3 month Treasury bills: 2.14%: 6 month Treasury bills: 2.04%: 1 year Treasury ... Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia Examples of zero-coupon bonds include US Treasury bills, US savings bonds, long-term zero-coupon bonds, and any type of coupon bond that has been stripped of its coupons. Zero coupon and deep discount bonds are terms that are used interchangeably. Treasury Bonds vs. Treasury Notes vs. Treasury Bills Treasury bonds, notes, and bills have zero default risk since they're guaranteed by the U.S. government. Investors will receive the bond's face value if held to maturity. However, if sold before... Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due.
US Treasury Bonds - Fidelity The coupon rate is fixed at the time of issuance and is paid every six months. Other Treasury securities, such as Treasury bills (which have maturities of one year or less) or zero-coupon bonds, do not pay a regular coupon. Instead, they are sold at a discount to their face (or par) value; investors receive the full face value at maturity.
United States Treasury security - Wikipedia Treasury bills (T-bills) are zero-coupon bonds that mature in one year or less. They are bought at a discount of the par value and, instead of paying a coupon interest, are eventually redeemed at that par value to create a positive yield to maturity.. Regular weekly T-bills are commonly issued with maturity dates of 4 weeks, 8 weeks, 13 weeks, 26 weeks, and 52 weeks.
Individual - Treasury Bonds: Rates & Terms Treasury Bonds: Rates & Terms Treasury bonds are issued in terms of 20 years and 30 years and are offered in multiples of $100. Price and Interest The price and interest rate of a bond are determined at auction. The price may be greater than, less than, or equal to the bond's par amount (or face value). (See rates in recent auctions .)
Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Best Differences (With ... - EDUCBA Treasury bond The bond is sold at their face value and has a fixed interest rate which is paid once every six months. Some of the key bonds are Municipal bonds, Governments bonds, corporate bonds, Zero Coupons bonds, etc. Bonds also called fixed-income instruments. Example:
Tax on US Treasury STRIPS | Finance - Zacks With a zero coupon Treasury bond, you must pay taxes on the imputed or phantom interest each year. The $100,000 STRIP purchased for $51,400 has a yield to maturity of about 3.3 percent; so in the ...
B treasury bills are zero coupon bonds c zero coupon B) Treasury bills are zero -coupon bonds. C) Zero -coupon bonds always trade at a discount. D) The yield to maturity is typically stated as an annual rate by multiplying the calculated YTM by the number of coupon payment per year, thereby converting it to an APR.
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia A zero-coupon bond, also known as an accrual bond, is a debt security that does not pay interest but instead trades at a deep discount, rendering a profit ...
Treasury Bills - Meaning, Types, Yield Calculation & How to Buy? Treasury bills are zero-coupon bonds, i.e. no interest is paid on them to investors. They are issued at a discount and redeemed at face value. Therefore, the returns earned by investors in T-bills remains fixed throughout the bond tenure irrespective of the economic condition of the country.
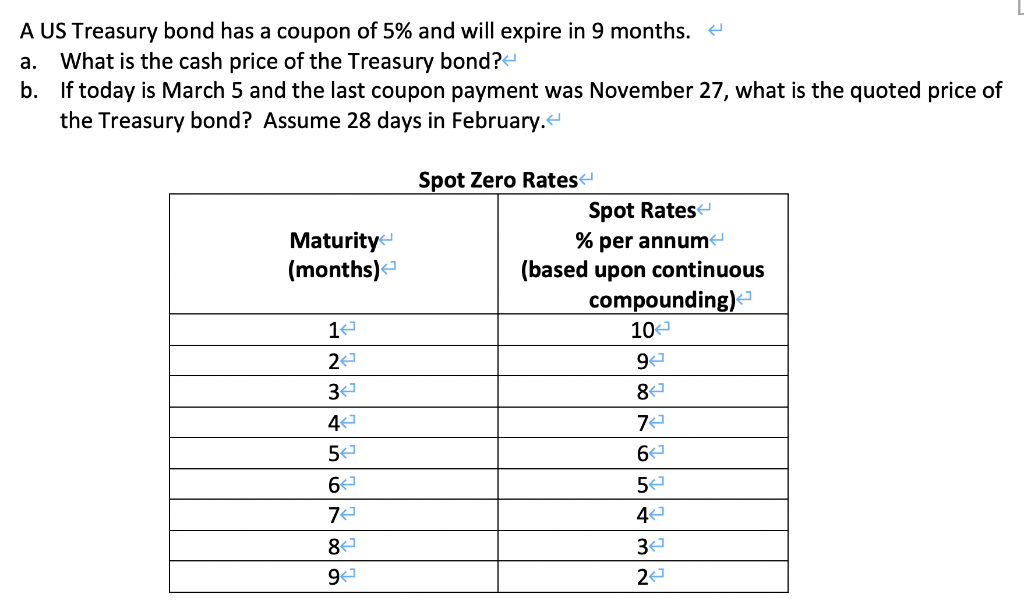
Government - Continued Treasury Zero Coupon Spot Rates* 3.20. 3.38. 3.79. *Four quarters covering calendar year 2012 and the first and second quarters of calendar year 2013 prepared by Economic Policy (EP) using the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) legacy model. Legacy model quarterly rates can be viewed within the "Selected Asset and Liability Price Report" under "Spot (Zero ...
Treasury Coupon Issues | U.S. Department of the Treasury Treasury Coupon Issues The Yield Curve for Treasury Nominal Coupon Issues (TNC yield curve) is derived from Treasury nominal notes and bonds. The Yield Curve for Treasury Real Coupon Issues (TRC yield curve) is derived from Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS).
Treasury Coupon Issues and Corporate Bond Yield Curves Treasury Coupon Issues Learn about the Treasury Yield Curves for Nominal and Real Coupon Issues (TNC and TRC yield curves) and The Treasury Breakeven Inflation Curve (TBI curve). Corporate Bond Yield Curve Papers and Data Learn about the corporate bond yield curve, and how it relates to the Pension Protection Act, by downloading these papers.
Treasury Bills (T-Bills) Definition - Investopedia T-bills are zero-coupon bonds that are usually sold at a discount and the difference between the purchase price and the par amount is your accrued interest. How Can I Buy a Treasury Bill? U.S....
Treasury Bills - Guide to Understanding How T-Bills Work T-bills, T-notes, and T-bonds are fixed-income investments issued by the US Department of the Treasury when the government needs to borrow money. They are all commonly referred to as "Treasuries." T-Bills Treasury bills have a maturity of one year or less, and they do not pay interest before the expiry of the maturity period.
Can you lose money on Treasury notes? - Note Brokering Treasury bills are not like coupon bonds that pay interest in accruals. What are Treasury bills example? Treasury bills are zero-coupon securities and do not pay interest. They are issued at a discount and are redeemed at face value at maturity. For example, a 91-day treasury bill of Rs. 100 / - (nominal value) can be issued for example Rs. ...
Treasury Bills (T-Bills) - Meaning, Examples, Calculations Treasury bills are a type of zero-coupon security where the central government borrows funds from the individual for a period of 364 days or less. ... another route is through the issue of T-Bills and other bonds Bonds Bonds refer to the debt instruments issued by governments or corporations to acquire investors' funds for a certain period ...
Zero Coupon Bond Funds: What Are They? - The Balance A zero coupon bond is a bond that doesn't offer interest payments but sells at a discount—a price lower than its face value. 1 The bondholder doesn't get paid while they own the bond, but when the bond matures, they will be repaid the full face value. Zero coupon bond funds are funds that hold these types of bonds.













Post a Comment for "41 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds"